What is a CNC Router and How Does It Work?
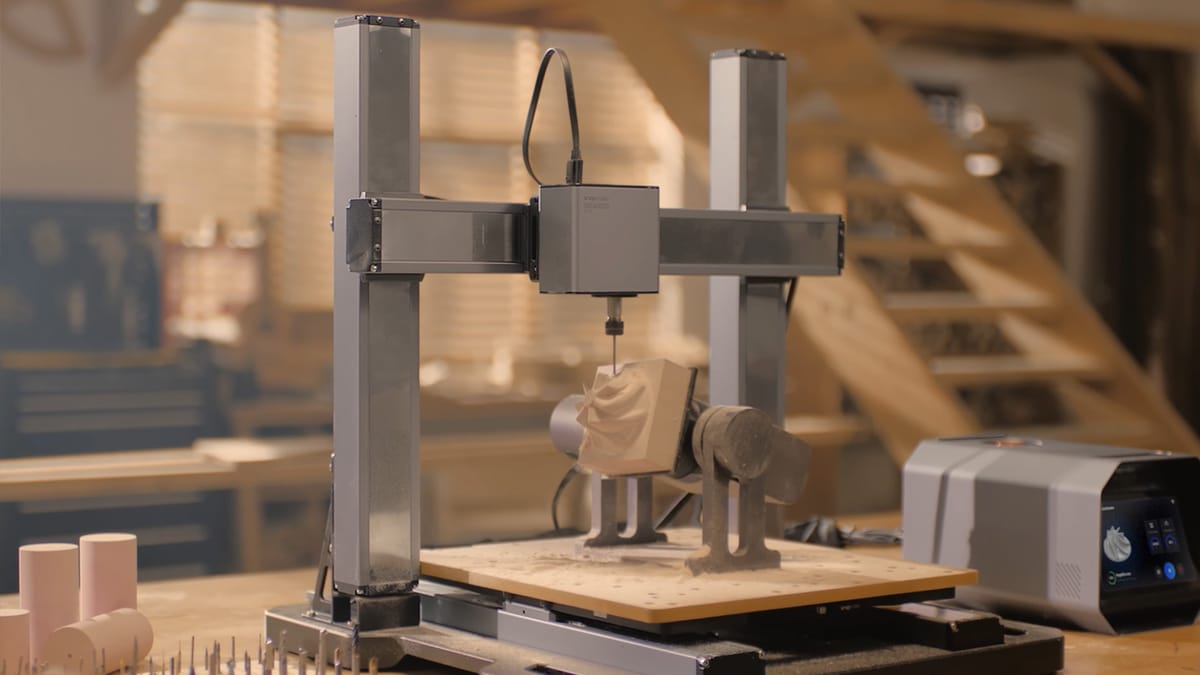

Indeed, in this world of automation and precision in manufacturing, CNC routers have become an integral part of the toolbox for the creator and manufacturers. Whether it is an amateur DIY-er who loves creating complex designs, a hobbyist who enjoys experimenting with creative possibilities, or a professional looking for extreme precision, CNC routers are the perfect link between technology and utility. Contrary to old-fashioned manual tools, CNC routers have the unique capability of completing very complex repeated operations with extreme accuracy. But how do they work, and what is a cnc router in depth?
Understanding CNC Routing
A CNC router is a computer-controlled machine that automatically cuts, carves, and shapes materials like wood, metal, plastic, and foam with precision. The "CNC" stands for Computer Numerical Control, which means the machine follows detailed digital instructions to create exactly what you want. It's like a handmade router, but with automation, allows doing things more quickly and accurately with very complex designs.
How it works:
- Design Creation: You start by designing something digitally in the CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software, which essentially is the blueprint for all the work involved after that.
- G-code Generation: The software converts that into G-code, which is the language used by CNC machines to get the machine to make the movements and do the operations.
- Machine Setup: Secure the material to the machine's work table. Attach the appropriate cutting tool, and set the zero point to align the machine's position with the design.
- Cutting Process: According to the provided G-code, the CNC-guided router will follow paths defined between portions to cut material to the prescribed design.
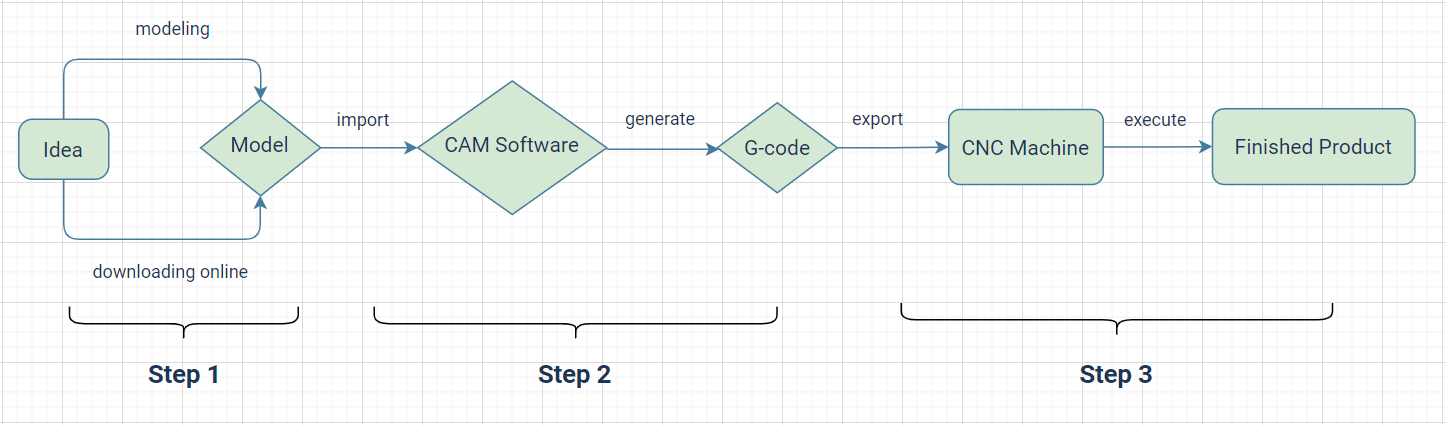
Decoding CNC Router Parts
Key components
- Spindle: The rotating tool responsible for cutting and carving material.
- Axes: Movement along X, Y, and Z axes enables precise 3D cutting and engraving.
- Controller: The machine’s brain, interpreting the G-code and directing the tool's movements.
- Frame and Table: The sturdy foundation that holds materials and supports the machine's operations.
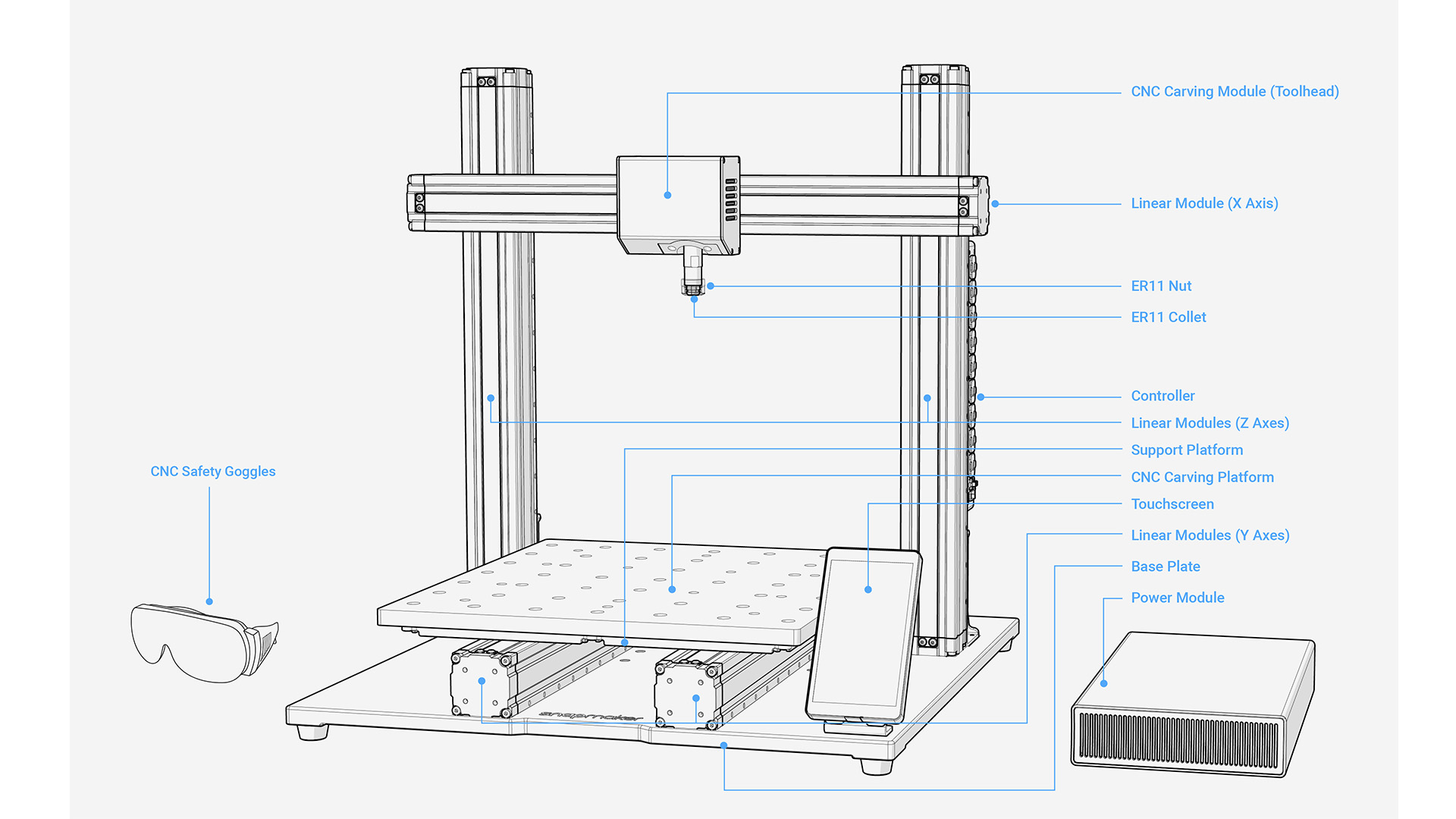
Tools and accessories
For cutting accurately, milling, or engraving, CNC employs several tools and accessories.
Router Bits and Collets
Milling bits and drill bits are two types of cutting tools.
- Milling bits include end mills, v-bits, and face mills for lateral cutting.
- Drill bits are designed for vertical plunging like drilling holes, plunging straight down into the material.
- Collets secure these bits in the spindle for accurate operation.
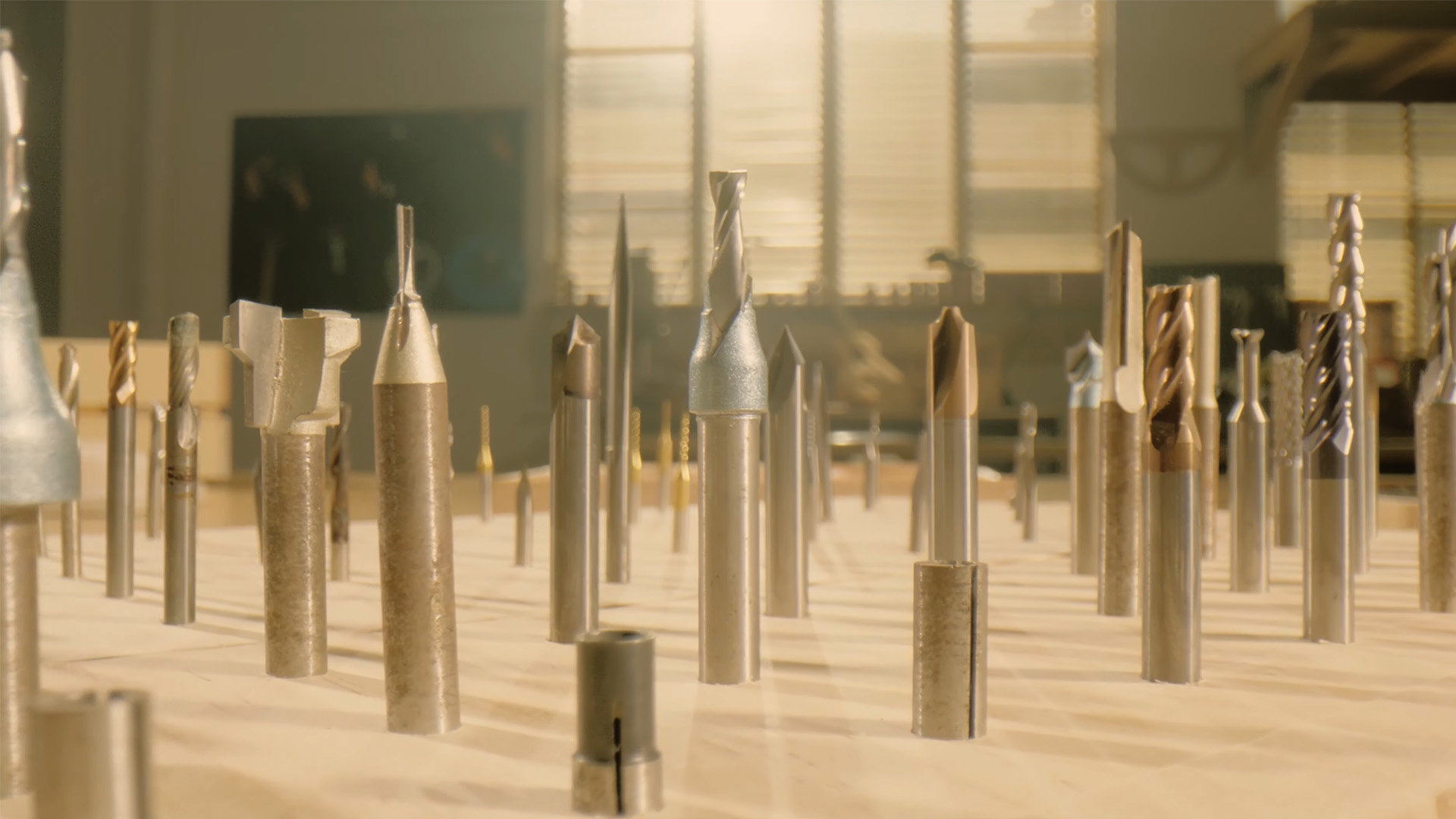
Workholding Devices
A CNC carver should be put on a sound and level workbench, and the workpieces should be held tightly in place during cutting.
- Vise: Used to hold workpieces securely in place.
- Clamps: Used to secure workpieces to the machine table.
- Vacuum Chuck: Used to hold flat workpieces securely.
Coolant and Dust Collection Systems
- Coolant Systems reduce heat and lubricate cutting surfaces.
- Carving will produce dirt and sawdust. Dust Collection Systems ensure clean workspaces and prevent debris from affecting performance.
Material Compatibility and Applications
CNC routers handle various materials, including wood, acrylic, foam, brass, and even softer metals like aluminum. So CNC machines are perfect for DIY furniture, sign-making, and custom parts. They’re also increasingly integrated with 3D printing for enhanced versatility in home workshops.
How to CNC Carve: A Step-by-Step Workflow Example
- Generate G-code
The first step is to design the object with CAD software and then convert the design to G-code with CAM software. G-code has very specific instructions for the CNC router, specifically its movements, speeds, and cutting depths. Verify the G-code to ensure it accurately represents your design and avoids potential errors during carving. - Fix the Material
Secure your material onto the CNC router's work table using appropriate holding methods, such as clamps, a vise, or a vacuum chuck. Properly fixing the material prevents it from shifting or vibrating, which can cause accuracy loss during the carving process. - Assemble the CNC Bit
Determine which cutting bit suits your work according to its material and design specifications. Place the bit in the spindle and clamp it into place firmly with a collet or chuck. Ensure the bit is aligned and installed to achieve precise cuts. - Set Work Origin and Start Carving
Position the CNC router exactly with its starting point aligned to the zero point of your design to establish where the work origin will be on the machine. Use the machine's controls to set the X, Y, and Z. Once everything is configured, start the carving process and monitor the machine closely to ensure smooth and accurate operation. - Finishing Touches
Disassemble the material from the working table after carving and check the piece for flaws. Rough edges can be sanded, dust or debris cleaned, and finishing techniques like painting, staining, or polishing applied for the final touches on the product.
CNC Router vs. CNC Mill
CNC routers and CNC mills are computer-controlled but are designed differently and have different aims. Here's a small overview of cnc router vs cnc mill.
● CNC Router: Softer materials such as wood, plastics, and foam are usually processed using CNC routers to make big emblems, pointers, or engravings. These machines operate at high cutting speeds and are suitable for two-dimensional and shallow three-dimensional operations. Routers can be very cheap and easy to maintain and are more commonly used by hobbyists and very small workshops.
● CNC Mill: CNC mills are set to cut harder materials, specifically metal. They operate at slower speeds with high torque for precision in deep cuts and complex shapes. In industrial settings, mills manufacture machine parts and other detailed projects.
Final thoughts
A CNC router is a game-changer for creators, combining precision, efficiency, and versatility. Indeed, with initial costs and learning curves, the advantages are much greater. This effect is especially remarkable in a person passionate about creating or conducting high-end production.
Whether you'll be carving your way to a very unusual DIY project or manufacturing extremely intricate parts, CNC routers will leave room for endless possibilities.
Ready to step into the world of CNC routing? Dive in and let your creativity take shape.




