Evolution of Dual Extrusion: A Complete Guide to Multi-Material 3D Printing

While single-extruder 3D printers are powerful tools, dual extrusion technology opens up a new dimension of creative and engineering possibilities. By employing two separate extruders, a printer can work with two materials in a single print job, unlocking advanced applications that are impossible with a single filament.
This guide will walk you through the evolution of this powerful technology, explain the key differences between the main approaches, and showcase how you can leverage dual extrusion for your most ambitious projects.
Why: Benefits of Dual Extrusion
Before diving into the technology, it's important to understand what makes it a game-changer. There are three primary benefits:
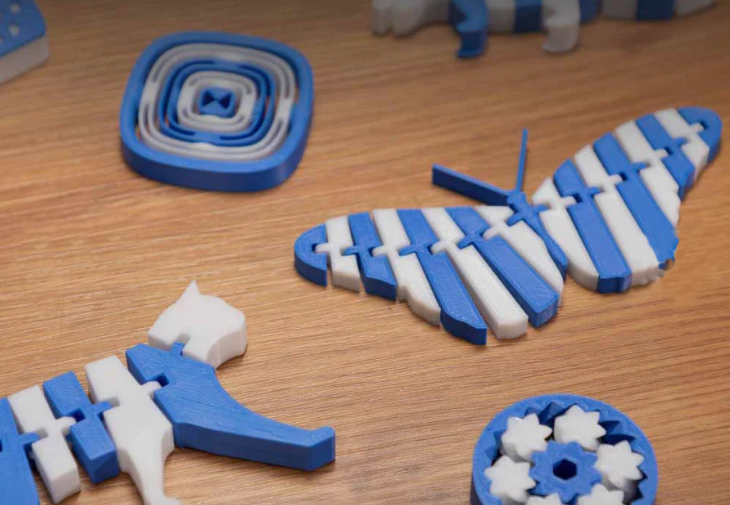

Multi-Color Printing
The most straightforward application is creating clean, sharp two-color models. This is perfect for printing logos, text, or aesthetic parts with distinct color separations without any need for post-processing or painting.
Complex Geometries with Soluble Supports
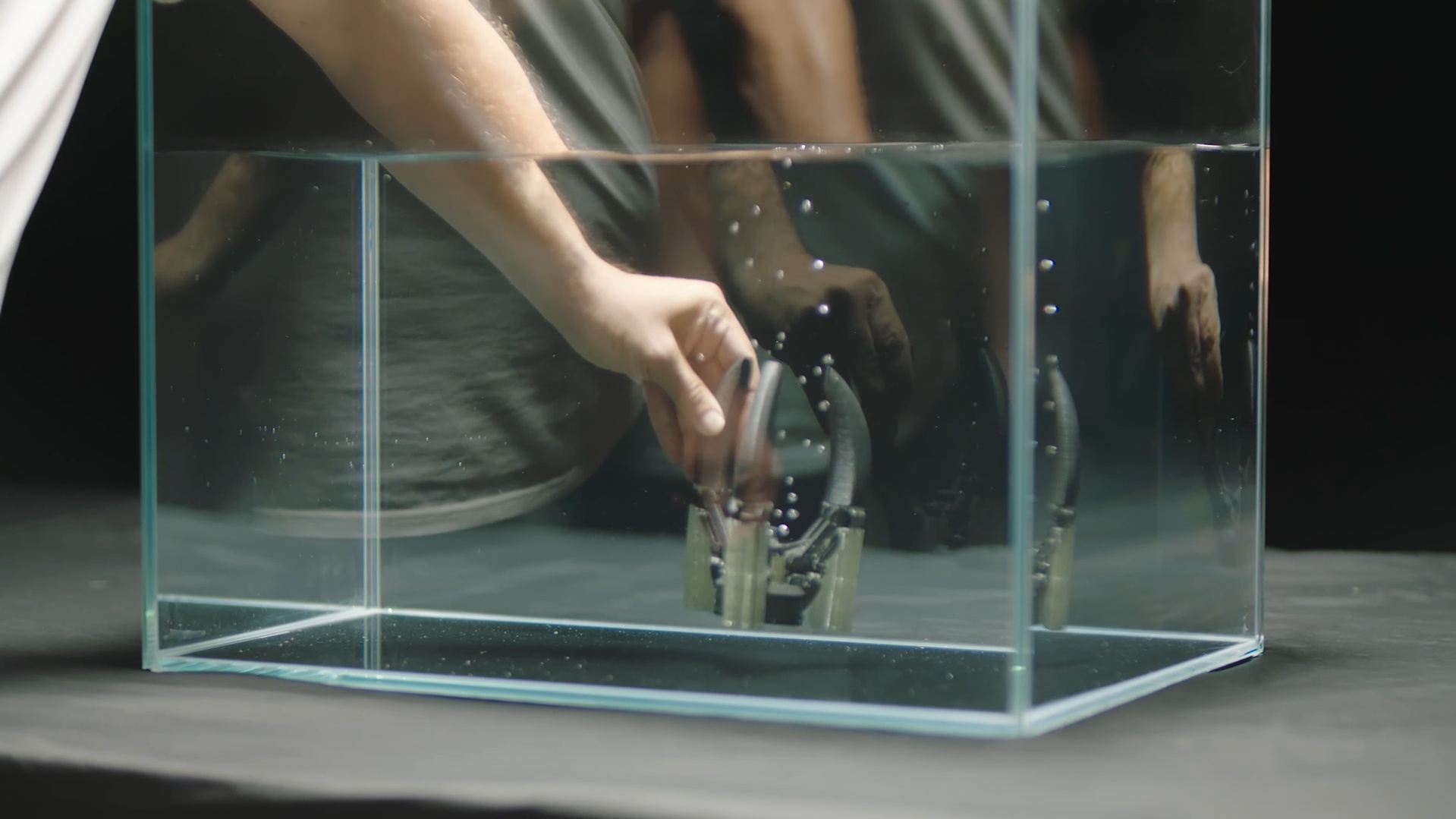

This is arguably the most powerful engineering application. For models with complex overhangs or intricate internal cavities, you can print the model in a standard material (like PLA) and the supports in a special water-soluble material (like PVA). After printing, you simply dissolve the supports in water, leaving a perfect, blemish-free surface that would be impossible to achieve with breakaway supports.
Advanced Multi-Material Printing
The goal here is to combine materials to create parts with hybrid properties, such as a rigid body with flexible elements. While powerful, this is one of the most challenging applications of desktop 3D printing. Success is highly dependent on material compatibility, as many common plastics do not adhere well to each other. Furthermore, different materials often require vastly different nozzle and bed temperatures, making it difficult to find settings that don't compromise the integrity of one or both filaments. Achieving good results requires significant expertise, careful selection of compatible filaments, and finely-tuned print profiles.
How: Two Paths to Dual Extrusion
Not all dual extruder systems are created equal. The technology has evolved along two major paths, each with distinct mechanics and advantages.
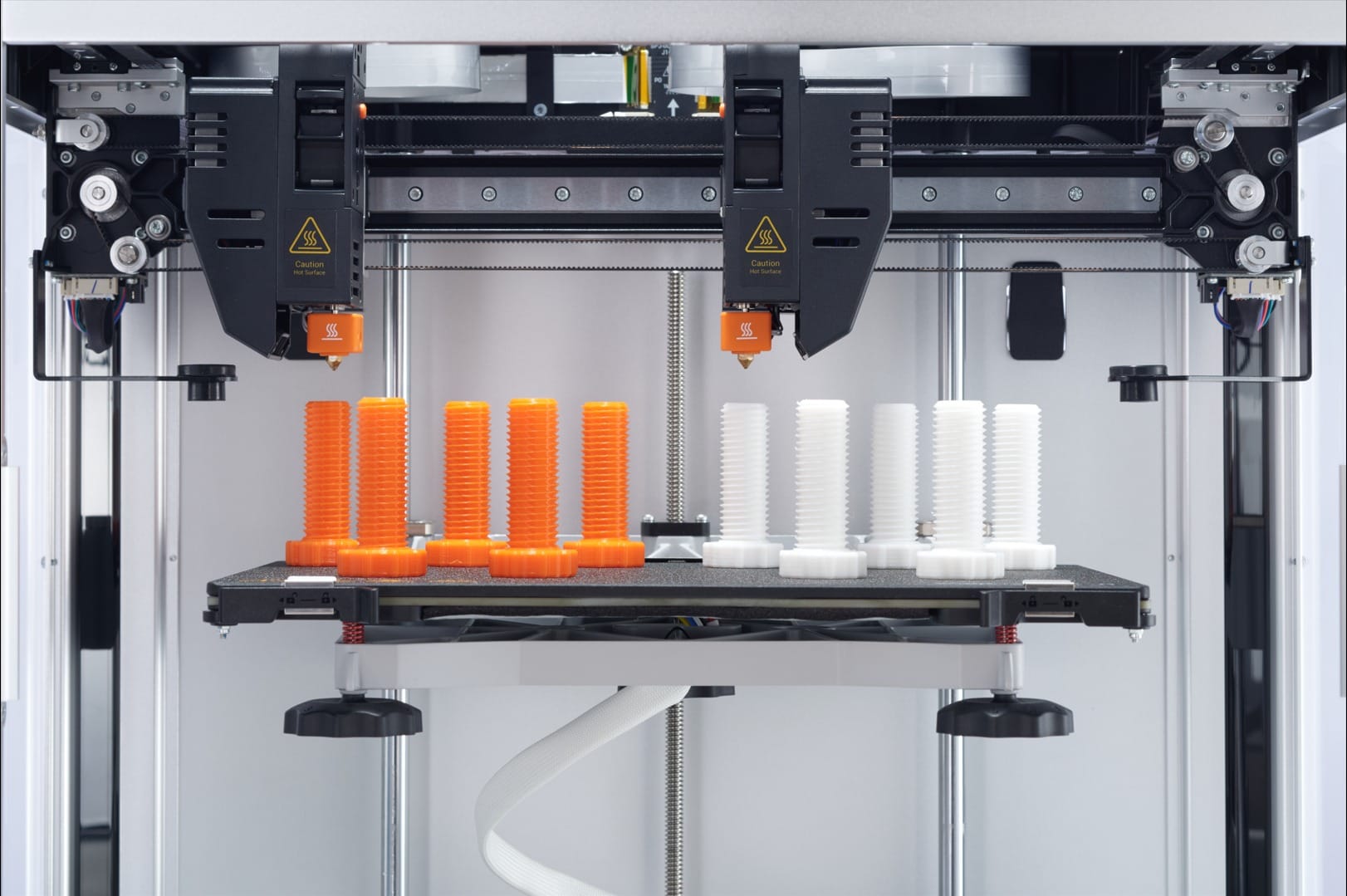
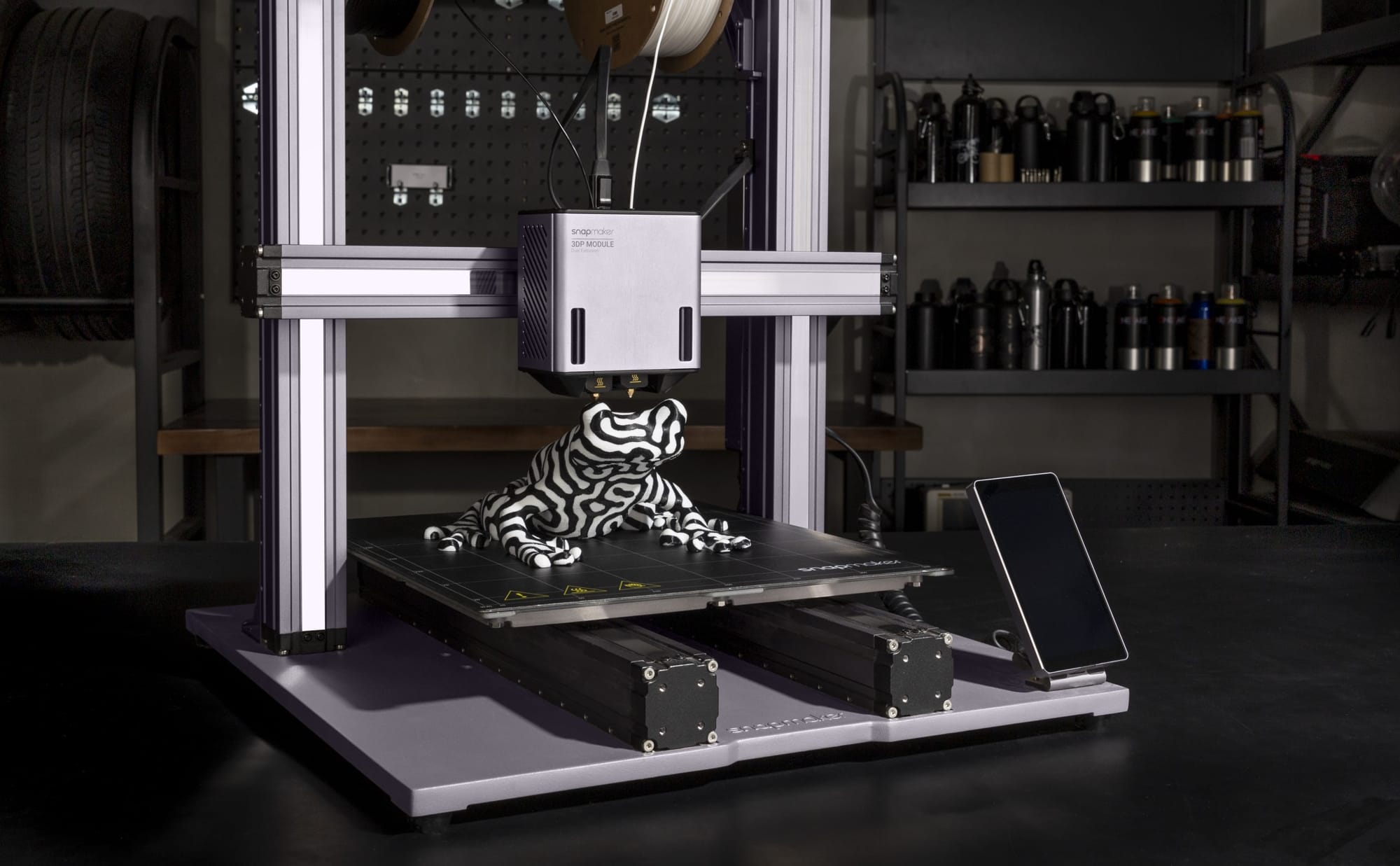


Compare IDEX (left) with single-head dual extruder (right).
IDEX Architecture - A Dedicated Solution for Speed and Precision
IDEX, or Independent Dual Extrusion, represents an advanced architecture where the printer is equipped with two print heads that can move independently of each other along the X-axis.
The Technology: This independence is a breakthrough. When one extruder is printing, the other can be "parked" entirely off to the side, away from the model. This completely eliminates the risk of the inactive hot nozzle oozing or dripping filament onto the print, which is the primary challenge of older systems. Furthermore, this architecture enables unique, high-efficiency production modes:
- Duplication Mode: Print two identical models simultaneously.
- Mirror Mode: Print a model and its perfect symmetrical counterpart at the same time.
Snapmaker's machine built around this technology was the Snapmaker J1s. It served as a powerful illustration of how the IDEX architecture could deliver high-speed, high-precision prints while enabling these advanced production modes.
Fixed Dual Extruders - The Classic Approach
The other major path to dual extrusion, and the most classic approach, uses two nozzles mounted together on a single, shared print head.
The Technology: While the nozzles move in unison, the printer intelligently switches which one is actively extruding filament. The primary technical challenge of this design is potential oozing from the hot, inactive nozzle. To manage this, modern systems are refined to use "prime towers" or "ooze shields"—extra structures printed alongside the model that wipe the nozzle clean before it begins a new color or material section.
While this technology is found on many dedicated printers, Snapmaker integrates it into a uniquely powerful and versatile ecosystem. On the Snapmaker Artisan, this capability is delivered via the swappable Dual Extrusion Module. The true power of this design is its modularity: the entire module can be seamlessly exchanged for a powerful 40W/10W laser engraving and cutting module or a robust 200W CNC carving and cutting module. This transforms a single machine into a complete digital fabrication workshop.
What's Next: Beyond Dual Extrusion
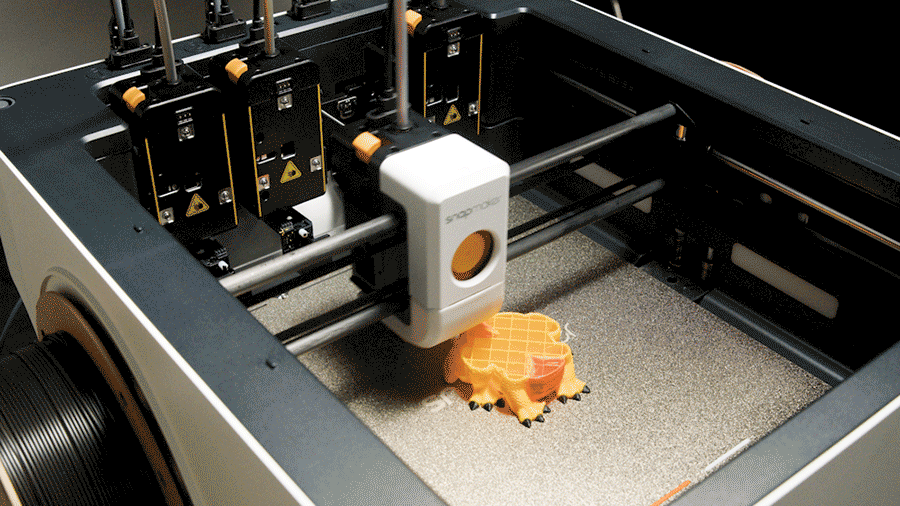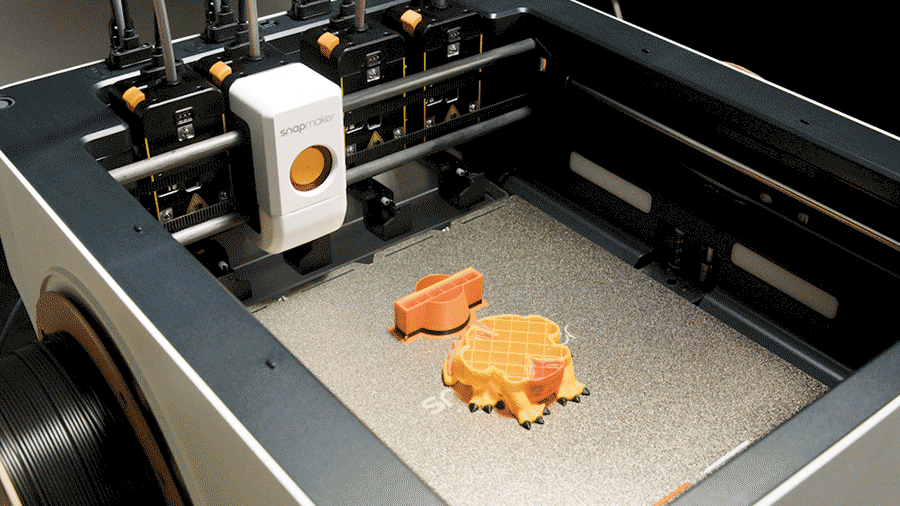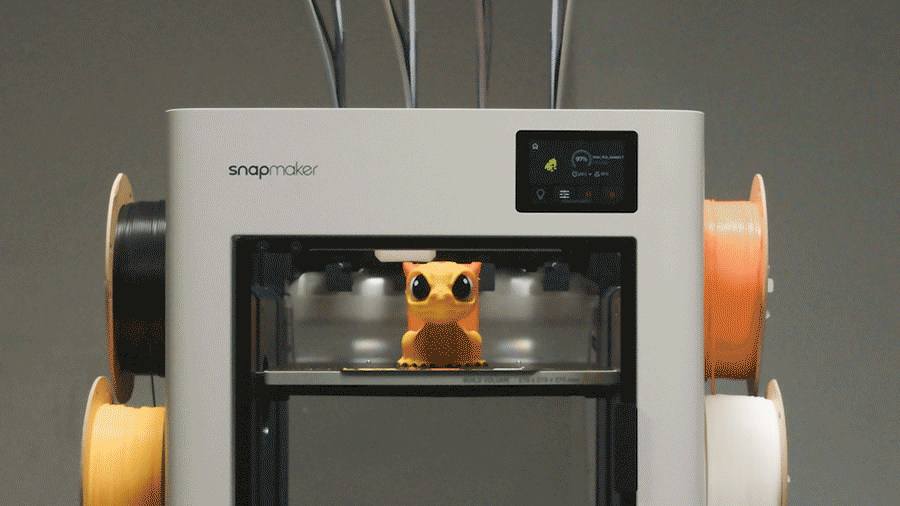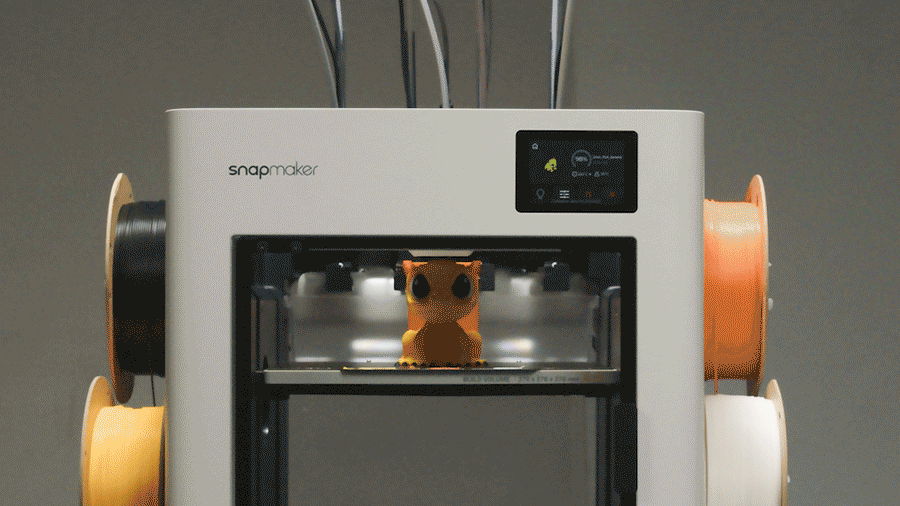
Dual extrusion is the perfect solution for working with two materials. But what happens when a project demands even more complexity—three, four, or even more materials in a single print? This question leads to the next frontier in multi-material innovation. For those needs, advanced systems like the Snapmaker U1, with its tool-changing capabilities, represent the future of automated, multi-color 3D printing.
Practical Guides for Dual Extrusion Success
Software is Key: Modern slicer software makes managing two extruders simple. In programs like Snapmaker Luban or the advanced Snapmaker Orca, you can easily assign different materials or colors to separate parts of a model and the software automatically generates the toolpaths and instructions for the printer.
Calibration is Critical: For any multi-nozzle system, precision is everything. You must perform an X/Y/Z offset calibration. This quick process tells the printer the exact distance between its two nozzle tips, ensuring that different materials line up perfectly with no gaps or overlaps.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What's the main difference between a regular dual extruder and an IDEX system?
A regular dual extruder has two nozzles fixed on the same print head that always move together. An IDEX system has two independent print heads that can move separately, which eliminates oozing and enables special production modes like printing two objects at once.
2. Do I need a dual extruder to print with dissolvable supports?
Yes. To print with a standard model material and a different dissolvable support material in the same job, a dual extruder printer is required. This is one of the most powerful reasons to upgrade to a dual extrusion system.
3. Is calibrating a dual extruder printer difficult?
While it requires an extra step, modern printers have made it much easier. The calibration process is largely automated and involves printing a test pattern and inputting some measurements into the machine. It typically only needs to be done once when setting up the machine.
4. Can I print with two different types of materials, like PLA and TPU, at the same time?
Yes, but it's an advanced technique. Success depends on using materials that are compatible, as many plastics don't adhere well to each other and require different print temperatures. It requires significant user expertise and experimentation to achieve good results.
5. Which Snapmaker machine is best for dual extrusion?
For users seeking the ultimate versatility of a complete workshop, the Snapmaker Artisan with its Dual Extrusion Module is the recommended choice. It brings high-quality dual extrusion to a proven platform that also excels at CNC carving and laser engraving.




