ABS vs. PLA 3D Printing Filaments: Characteristics, Best Printing Practices
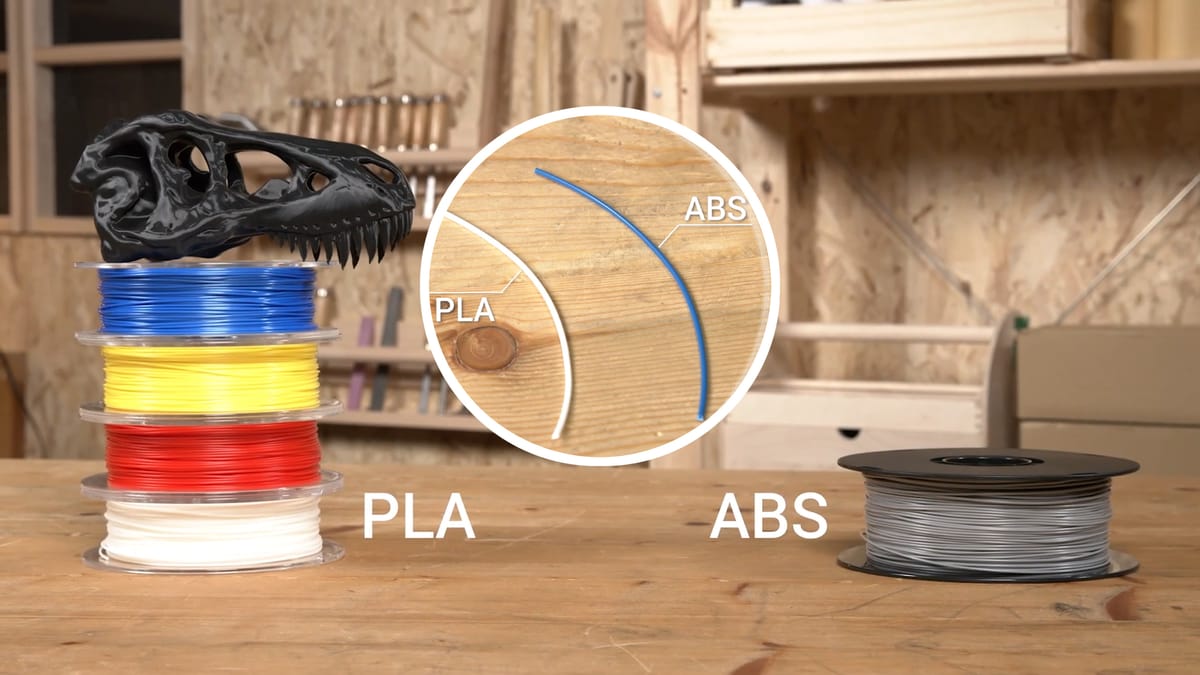
ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) and PLA (polylactic acid) are among the most extensively used 3D printing filaments in FDM printing. Every material has distinct features influencing the prints' quality, strength, and usability. Thus, knowing which materials are different, their properties, and how to use them is important, especially when using Snapmaker products. Whether for leisure or work, this guide will help weigh the pros and cons of ABS and PLA, aiding effective printing decisions.
The Quick Answer: ABS vs. PLA
For those who need a fast answer, here is a quick summary of the key differences:
Feature | PLA (Polylactic Acid) | ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) |
Ease of Printing | Easy. Very forgiving, low warping, no enclosure needed. | Challenging. Prone to warping, requires a heated bed and enclosure. |
Strength Type | High Tensile Strength. Rigid and stiff, but brittle. | High Impact Strength. Tough, durable, and more flexible. |
Temperature Resistance | Low. Begins to soften and deform around 60°C (140°F). | High. Withstands temperatures up to 100°C (212°F). |
Detail & Finish | Excellent. Capable of very sharp details and clean finishes. | Good. Can be smoothed with acetone for a glossy finish. |
Safety (Fumes) | Low Odor. Emits a mild, slightly sweet smell. | Strong Odor. Releases potentially harmful fumes (VOCs) and requires good ventilation. |
Material Properties: ABS vs. PLA
Before weighing between 3d printer filament ABS vs. PLA, one must first understand the features of the two materials. To this end, ABS is a thermoplastic polymer with strength, flexibility, and impact resistance and can withstand mechanical shock.
ABS's high melting point makes it suitable for making automotive components and domestic wares, but the higher temperatures also lead to the release of harmful gasses during the printing process, which requires good ventilation.
PLA is a biodegradable plastic that can be made from cornstarch and other safe materials. It is a low-cost filament that is virtually simple to use and does not require a heated bed or excessively high temperatures. Despite not being as strong or flexible as ABS, PLA has no unpleasant smells, ensuring easy use for fresh beginners and eco-friendly consumers.
For now, let’s move on to the aspects of each material.
Note: The information in this article applies to Snapmaker materials.
| Property | ABS | PLA |
| Tensile Strength | 33.3 ± 0.8 MPa | 46.6 ± 0.9 Mpa |
| Charpy Impact Strength | 12.6 ± 1.1 kJ/㎡ | 2.7 ± 0.2 kJ/㎡ |
| Durability | Long-lasting and weather-resistant | Less durable and prone to wear |
| UV Resistance | Moderate, can yellow over time | Weak, fade in sunlight |
| Chemical Resistance | Good with oils and acids | Poor chemical resistance |
| Temperature Resistance | It withstands up to 100°C | Lower, begins to soften around 60°C |
| Hygroscopy | Absorbs more moisture; careful storage is needed | Absorbs minimal moisture |
| Food Safety | Food-safe | Generally food-safe, but depends on additives |
Related reading: Are the Odors Released During 3D Printing Toxic?
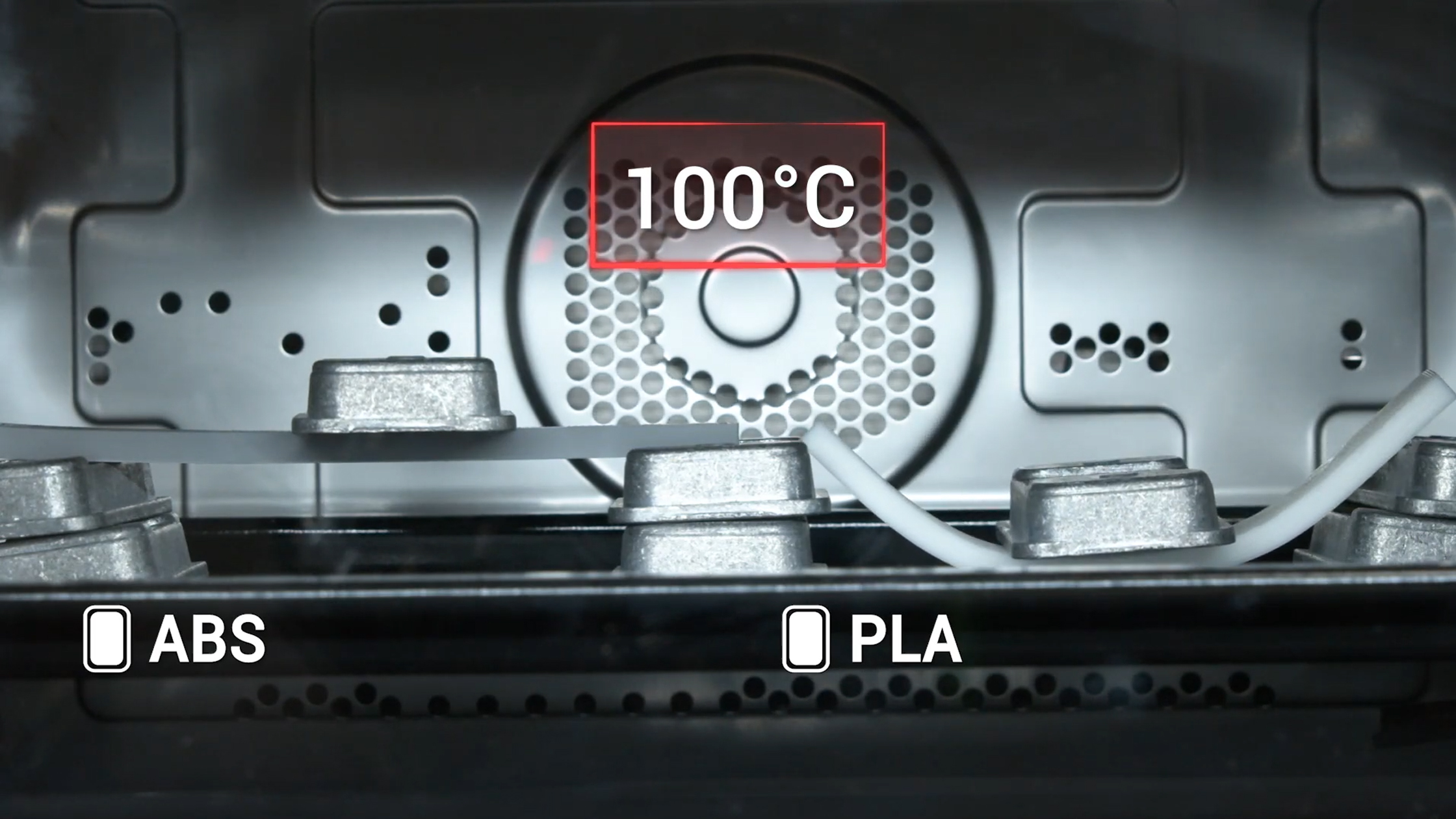
Tensile Strength
In terms of tensile strength, PLA (46.6 ± 0.9 MPa) surpasses ABS (33.3 ± 0.8 MPa), which makes it more appropriate for such projects. ABS's tensile strength may be lower, but its composition can bend, so it does not easily break under pressure.
Charpy Impact Strength
ABS excels in Charpy impact strength (12.6 ± 1.1 kJ/㎡), ideal for parts that withstand bumps or drops. PLA, with a lower impact strength (2.7 ± 0.2 kJ/㎡), is more brittle and can easily fracture upon impact, making it best for decorative or light-duty parts.
Durability
ABS is highly durable and weather-resistant, making it a solid choice for outdoor or functional parts. PLA, while easier to print, is less durable and better suited for indoor applications or aesthetic pieces that don’t experience much wear.
UV Resistance
ABS offers moderate UV resistance but may become yellow over time. PLA has weak UV resistance, fading and degrading quickly when exposed to sunlight, making it suitable only for indoor or shaded applications.
Chemical Resistance
ABS performs well even in industrial environments due to its resistance to oils and acids. On the other hand, PLA lacks these qualities and, therefore, is more likely to be eroded when chemicals are present.
Temperature Resistance
ABS can tolerate higher temperatures, staying stable up to around 100°C, making it suitable for parts that may face heat exposure. PLA softens at lower temperatures (around 60°C) and is more likely to deform in warmer settings.
Hygroscopy
PLA absorbs more moisture than ABS, making it essential to store PLA carefully to prevent printing issues. ABS is less hygroscopic, but both materials benefit from dry storage to maintain print quality.
Food Safety
Usually, containers made of ABS and PLA are food-safe, though this will depend on the materials used. PLA is more or less okay to use for things that involve contact with food, but it is still wise to consult the manufacturer before proceeding with prints that will come into contact with any food.
Upgrading Your PLA Prints
Within the PLA family, specialized options can further enhance your projects:
- For prints where visual appearance is paramount, materials like Matte PLA offer a beautiful, non-reflective finish that helps hide layer lines and gives a professional, high-quality look.
- And for projects where speed is the priority, specialized filaments like High-Speed PLA enable rapid prototyping without sacrificing print quality.
Best Printing Practices for PLA and ABS
Printing Parameter
- ABS: The print temperature is generally between 220 °C and 250°C. To reduce the chances of warping, a heated bed (80-110 degrees Celsius) is important, and an enclosure can assist in maintaining the temperature. Good ventilation is also recommended, as ABS emits fumes.
- PLA: The 3D printing temperature typically ranges from 180°C to 220°C. PLA doesn’t necessarily require a heated bed, though setting it between 40 °C and 60°C can improve adhesion. An enclosure isn't necessary since PLA doesn’t emit strong odors, making it ideal for open spaces.
Tips for Successful Prints
- ABS: To avoid warping, apply an adhesive layer on the bed and use a print enclosure to maintain consistent temperatures. Snapmaker’s video tutorial offers helpful guidelines for working with ABS.
- PLA: PLA can be printed on an open bed but may benefit from a slight temperature boost to enhance adhesion. Although it’s easier to print than ABS, PLA prints can be brittle and should be stored carefully to avoid moisture buildup.
Final thoughts
Choosing between ABS and PLA depends on your project requirements and experience level. While ABS is robust and long-lasting, it requires careful handling and safety precautions. PLA, by contrast, is eco-friendly and user-friendly and an excellent choice for simple projects or decorative items. Consider using materials from Snapmaker to ensure success, as quality can significantly impact your results. If you wonder how much 3D printer filament costs, you may check out our materials store.
FAQs
Is ABS stronger than PLA? It depends on the type of strength. PLA has higher tensile strength, meaning it's more rigid and resists being pulled apart. ABS has higher impact strength, meaning it's tougher and can bend and absorb impacts without shattering. For a decorative statue, PLA is "stronger." For a drone frame that needs to survive a crash, ABS is "stronger."
Do I really need an enclosure to print ABS? While it's possible to print small ABS parts without one, an enclosure is highly recommended for consistent success. It dramatically reduces the chance of warping and layer splitting, especially on larger prints, and helps contain the fumes.
Is it safe to 3D print with PLA indoors? Yes, PLA is generally considered safe for printing indoors without special ventilation, thanks to its low emission of VOCs and mild odor. However, ensuring good general air circulation in your room is always a good idea.
Can I use PLA for parts that will be in a hot car? No. PLA has a low glass transition temperature of around 60°C (140°F). On a hot day, the interior of a car can easily exceed this temperature, which will cause PLA parts to soften, warp, and deform. ABS is the correct material for this application.
What is the strongest 3D printer filament? The "strongest" is hard to define. However, some materials are commonly considered the strongest among easily accessible filaments: Polycarbonate (PC), Polyamide(Nylon), and Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Filaments.
Can moist PLA or ABS cause clogging? Yes, moist PLA or ABS can indeed cause clogging in 3D printers. When filament absorbs moisture, it can lead to several issues: Bubbles Formation, Nozzle Clogging, and Filament Swelling. It's crucial to keep your filament dry.
Recommended reading: How to Store Your 3D Printer Filament and Prevent Moisture




